Lab 12: Recursive Number Sequences
The main goal this lab is for you to get a more practice with recursion.
Introductions
Introduce yourself to your lab partner(s). Are you ready for final exams?
Recursion Tips
What is the base case or cases? What is the simplest instance of the problem you can solve?
What is the recursive step?
Mathematical Background
The natural numbers are the integer sequence \[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, \ldots \] and can be defined recursively as \[ \text{Nat}(n) = \begin{cases} 0 & \text{ if $n = 0$} \\ 1+ \text{Nat}(n-1) & n > 0 \end{cases}. \] This is sequence A001477 in the Online Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS).
The square numbers are the integer sequence \[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, \ldots \] and can be defined recursively as \[ \text{Sq}(n) = \begin{cases} 0 & \text{ if $n = 0$} \\ 1 + 2(n-1) + \text{Sq}(n-1) & n > 0 \end{cases}. \] This is sequence A000290 in the OEIS.
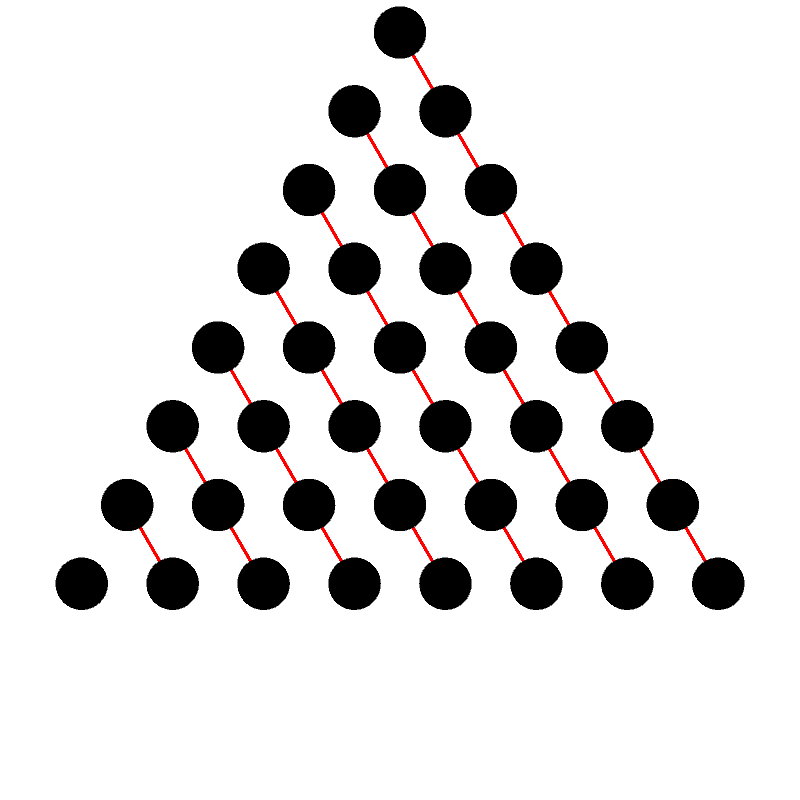
The triangular numbers are the integer sequence \[0, 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 28, 36, 45, 55, \ldots \] and can be defined recursively as \[ \text{Tri}(n) = \begin{cases} 0 & \text{ if $n = 0$} \\ n + \text{Tri}(n-1) & n > 0 \end{cases}. \] This is sequence A000217 in the OEIS.
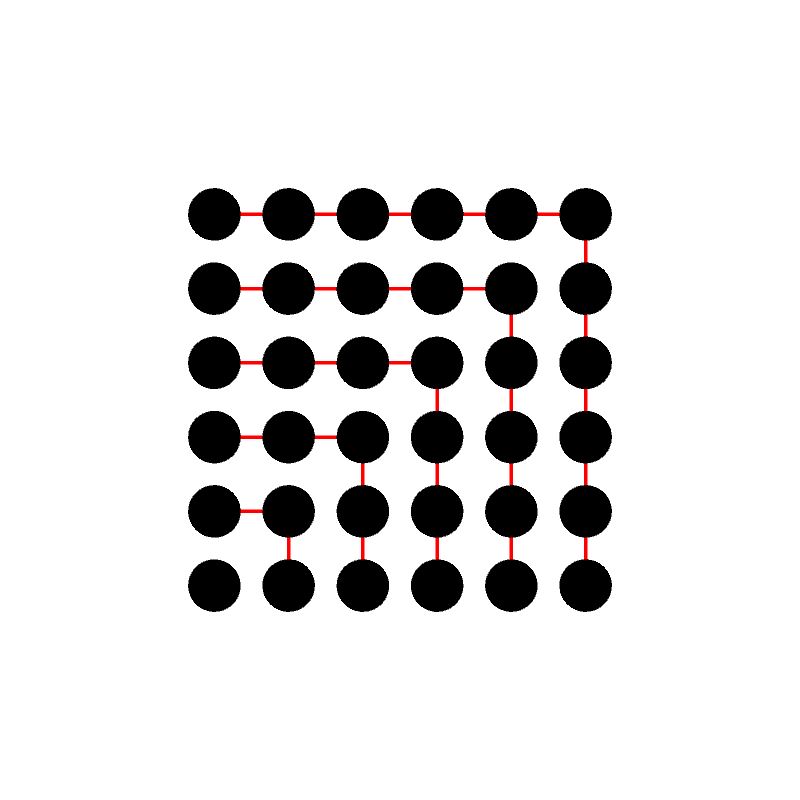
The number of moves required to solve an \(n\) height Towers of Hanoi puzzle is the integer sequence \[0, 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, 1023, \ldots \] and can be defined recursively as \[ \text{Moves}(n) = \begin{cases} 0 & \text{ if $n = 0$} \\ 1 + 2\cdot\text{Moves}(n-1) & n > 0 \end{cases}. \] This is sequence A000225 in the OEIS.
The Narayana's Cows sequence is the integer sequence \[1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 13, 19, 28, \ldots \] and can be defined recursively as \[ \text{Cows}(n) = \begin{cases} 1 & \text{ if $n \le 2$} \\ \text{Cows}(n-1) + \text{Cows}(n-3) & n \gt 2 \end{cases}. \] This is sequence A000930 in the OEIS.
The number of Derangements is given by the integer sequence \[1, 0, 1, 2, 9, 44, 265, 1854, 14833, 133496, \ldots \] and can be defined recursively as \[ \text{Der}(n) = \begin{cases} 1 & \text{ if $n = 0$} \\ 0 & \text{ if $n = 1$} \\ (n-1)\left(\text{Der}(n-1) + \text{Der}(n-2)\right) & n \ge 2 \end{cases}. \] This is sequence A000166 in the OEIS.
The centered hexagonal numbers are the integer sequence \[1, 7, 19, 37, 61, 91, 127, 169, 217, 271, \ldots \] and can be defined recursively as \[ \text{Hex}(n) = \begin{cases} 1 & \text{ if $n = 0$} \\ \text{Hex}(n-1) + 6n & n \gt 0 \end{cases}. \] This is sequence A003215 in the OEIS.
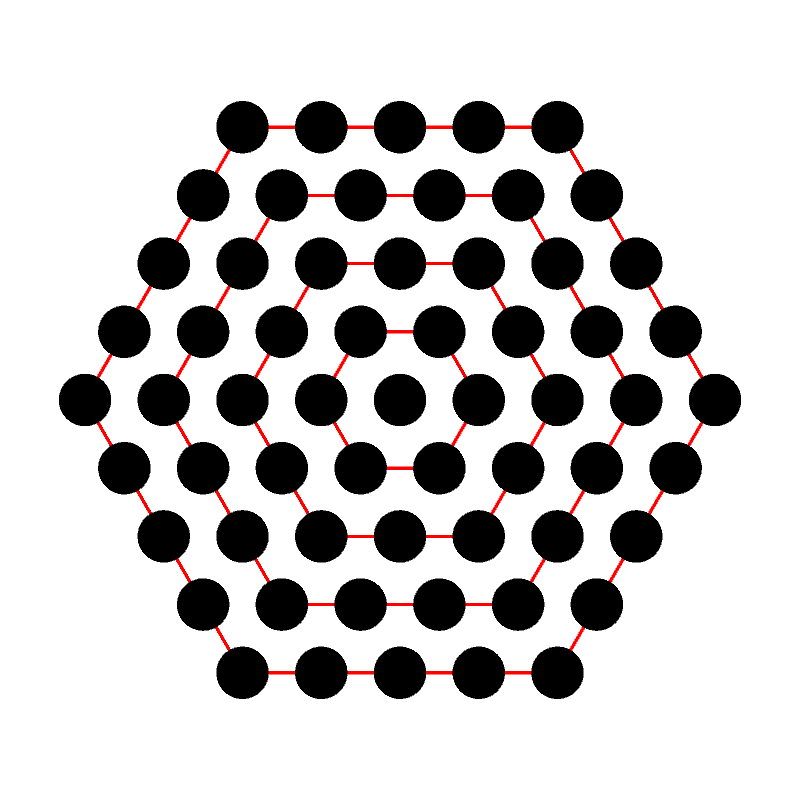
The Tetrahedral Numbers are the integer sequence \[0, 1, 4, 10, 20, 35, 56, 84, 120, 165, 220, \ldots \] and can be defined recursively as \[ \text{Tetra}(n) = \begin{cases} 0 & \text{ if $n = 0$} \\ \text{Tetra}(n-1) + \text{Tri}(n) & n \gt 0 \end{cases}. \] This is sequence A000292 in the OEIS.
The Square Pyramidal Numbers are the integer sequence \[0, 1, 5, 14, 30, 55, 91, 140, 204, 285, 385, \ldots \] and can be defined recursively as \[ \text{SqPyr}(n) = \begin{cases} 0 & \text{ if $n = 0$} \\ \text{SqPyr}(n-1) + \text{Sq}(n) & n \gt 0 \end{cases}. \] This is sequence A000330 in the OEIS.
The Star Numbers are the integer sequence \[1, 13, 37, 73, 121, 181, 253, 337, 433, 541, 661, 793, \ldots \] and can be defined recursively as \[ \text{Star}(n) = \begin{cases} 1 & \text{ if $n = 0$} \\ \text{Star}(n-1) + 6\cdot 2\cdot n & n \gt 0 \end{cases}. \] This is sequence A003154 in the OEIS.
The Catalan Numbers are the integer sequence \[1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, \ldots \] and can be defined recursively as \[ \text{C}(n) = \begin{cases} 1 & \text{ if $n = 0$} \\ \displaystyle\sum_{i=0}^{n-1} C(i)\cdot C(n-1-i)& n \gt 0 \end{cases}. \] Recall that the summation notation \(\sum\) is just representing adding the terms as you would in a for loop. For example, \[ \begin{split} \text{C}(1) &= \text{C}(0)\text{C}(0) = 1\\ \text{C}(2) & = \text{C}(0)\text{C}(1) + \text{C}(1)\text{C}(0) = 2\\ \text{C}(3) & = \text{C}(0)\text{C}(2) + \text{C}(1)\text{C}(1) + \text{C}(2)\text{C}(0) = 5\\ & \vdots \\ \text{C}(n) & = \underbrace{\text{C}(0)\text{C}(n-1) + \text{C}(1)\text{C}(n-2) + \cdots + \text{C}(n-2)\text{C}(1) + \text{C}(n-1)\text{C}(0)}_{n \textrm{ terms}} \end{split} \] This is sequence A000108 in the OEIS.
Task
Complete the methods in Lab12.py, as shown below. Don't use any for loops except as noted
# Lab 13
# Number sequences
# YOUR NAMES AND EMAIL HERE!
# Natural numbers - RECURSIVELY!
# https://oeis.org/A001477
def nat(n):
return 0
# Square numbers - RECURSIVELY!
# https://oeis.org/A000290
def sq(n):
return 0
# Triangular numbers - RECURSIVELY!
# https://oeis.org/A000217
def tri(n):
return 0
# Towers of Hanoi moves - RECURSIVELY!
# https://oeis.org/A000225
def moves(n):
return 0
# Narayana's Cows - RECURSIVELY!
# https://oeis.org/A000930
# https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VOS3piSMS9E
# https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6yXQinqLmqc
# https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sRvH6ZhojqA
def cows(n):
return 0
# Derangements - RECURSIVELY!
# https://oeis.org/A000166
def der(n):
return 0
# Centered Hexagonal Numbers - RECURSIVELY!
# https://oeis.org/A003215
def hex(n):
return 0
# Tetrahedral Numbers - RECURSIVELY!
# https://oeis.org/A000292
def tetra(n):
return 0
# Square Pyramidal Numbers - RECURSIVELY!
# https://oeis.org/A000330
def sqpyr(n):
return 0
# Star Numbers - RECURSIVELY!
# https://oeis.org/A003154
def star(n):
return 0
# Catalan Numbers - mostly RECURSIVE!
# use a loop for the summation
# https://oeis.org/A000108
def cat(n):
return 0
def main():
print("naturals")
print("[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, ...]")
seq = list()
for i in range(20):
seq.append(nat(i))
print(seq)
print()
print("squares")
print("[0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, ...]")
seq = list()
for i in range(20):
seq.append(sq(i))
print(seq)
print()
print("triangular")
print("[0, 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 28, 36, 45, 55, ...]")
seq = list()
for i in range(20):
seq.append(tri(i))
print(seq)
print()
print("Towers of Hanoi moves")
print("[0, 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, 1023, ...]")
seq = list()
for i in range(20):
seq.append(moves(i))
print(seq)
print()
print("Narayana's Cows")
print("[1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 13, 19, 28, ...]")
seq = list()
for i in range(20):
seq.append(cows(i))
print(seq)
print()
print("Derangements")
print("[1, 0, 1, 2, 9, 44, 265, 1854, 14833, 133496, ...]")
seq = list()
for i in range(12):
seq.append(der(i))
print(seq)
print()
print("Centered Hexagonal Numbers")
print("[1, 7, 19, 37, 61, 91, 127, 169, 217, 271, ...]")
seq = list()
for i in range(20):
seq.append(hex(i))
print(seq)
print()
print("Tetrahedral Numbers")
print("[0, 1, 4, 10, 20, 35, 56, 84, 120, 165, 220, ...]")
seq = list()
for i in range(20):
seq.append(tetra(i))
print(seq)
print()
print("Square Pyramidal Numbers")
print("[0, 1, 5, 14, 30, 55, 91, 140, 204, 285, 385, ...]")
seq = list()
for i in range(20):
seq.append(sqpyr(i))
print(seq)
print()
print("Star Numbers")
print("[1, 13, 37, 73, 121, 181, 253, 337, 433, 541, 661, 793, ...]")
seq = list()
for i in range(20):
seq.append(star(i))
print(seq)
print()
print("Catalan Numbers")
print("[1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, ...]")
seq = list()
for i in range(11):
seq.append(cat(i))
print(seq)
main()
When you are finished, email your lab files to your lab partner(s) and instructor.